#Cybersecurity

05/11/2025
For CISOs, the approach of the holiday season often coincides with the preparation of capital expenditure (CAPEX) budgets for the following year.
This can be a tricky negotiation, especially when you’re trying to convince your management to increase cybersecurity spending.
While most organizations now recognize the need to invest in IT security solutions, opinions differ on how much funding should be allocated to this expense.
A random amount, set at 10% of the IT investment budget, has sometimes been used as the basis for this calculation. But this arbitrary percentage varies, of course, from one organization to another.
CISOs are therefore faced with a challenge: how can they convince senior management, who are removed from the realities on the ground and lack technical knowledge, of the benefits of increasing their cybersecurity spending?
At Rsecure, we take a pragmatic approach to this discussion, correlating IT security risks with the interests of senior management.
Here’s how.

Through these objections, executive committees are fulfilling their role as managers seeking to allocate the limited resources at their disposal in the best possible way to meet all of the company’s investment needs.
These obstacles faced by CISOs slow down the deployment of cybersecurity projects, which are essential for data protection and, ultimately, the sustainability of the organization.
If even the most flawless technical demonstrations are not enough to convince your management to release budgets, it may be worth taking a different approach.
To convince a manager, we recommend refocusing your messages and providing context: what would happen if production lines were shut down for a week following a ransomware attack? How much does it cost to have a team shut down for just half a day? How much do your managers estimate the impact of these disruptions on business, customer relations, and the company’s reputation?
The challenge is not to defend cybersecurity solutions, but to get your management team to consider the concrete consequences of an incident, in order to compare the cost of a preventive investment with that of a crisis to be managed.
Let’s discuss your cybersecurity now!
When addressing the topic of cybersecurity, we recommend making it understandable to everyone. To do this, you need to be didactic and avoid technical jargon in favor of general concepts.
The benefits of a SOC, EDR, or cyber monitoring solution are not limited to noise reduction, better protection of company data, or a reduction in the attack surface exposed to cybercriminals.
To be understood, we recommend translating these technical benefits into financial, operational, and legal impacts.
You need to make your executives understand that cybersecurity enables :
To illustrate this approach in concrete terms, here are a few ideas to discuss with your executive committee, without resorting to technical jargon.
Remember that IT is no longer a subject “for geeks,” but the backbone of business activity.
Do your contacts not see it that way? Ask them a simple question: which important services or functions would continue to operate normally in the event of a major outage due to a cyberattack? The answer: almost none.
From billing to payroll, from commercial exchanges to modern production lines, all operations depend on digital tools that must remain operational.
To do this, we recommend mapping IT risks and highlighting the danger of a cyberattack compared to, for example, a weather hazard.
Calculate the precise cost of a cybersecurity incident. In very concrete terms, this translates into downtime and lost productivity, plus a long list of associated costs :
Costs incurred and not controlled by the company, which will then find itself in a crisis management situation.
Presented in a simple and factual manner, these calculations highlight the direct impact of a cybersecurity incident on margins.
On the one hand, even a temporary interruption of services leads to a drop in revenue, while fixed costs (salaries, rent, subscriptions) remain unchanged. On the other hand, disruptions due to inaccessible tools inevitably cause productivity losses and sometimes additional expenses to make up for production delays.
Corrective actions, which are essential in times of crisis, automatically reduce overall profitability.
Will the company be able to absorb the impact of a cyberattack ?
At this point, your audience should understand the importance of investing in cybersecurity. However, there is still one persistent objection to overcome: “Is it really necessary? We’ve never been attacked.”
Without being alarmist, respond by putting the risk into context. Stick to the facts and give examples of companies similar to yours: same industry, same region, same type of business, or even same tools used.
The local and national press regularly reports on cyberattacks that can support your case studies.
In the industry, we remember the Pierre Fabre group, which in 2021 suffered a near-complete shutdown of its systems : no website, no switchboard, and a French production line that was completely shut down for weeks.
Local authorities such as the Normandy Region in France, essential service providers such as Rouen University Hospital, and major economic players such as POST and Luxembourg government departments are regularly crippled by targeted cyberattacks and ransomware.
When a cyberattack occurs, companies’ data and communication networks are often cut off.
Employees then have to resort to taking notes on paper, buying emergency equipment from retailers aimed at the general public, and using personal email accounts to continue working.
The impact on service quality, business continuity, and the company’s image can be significant.
Presenting these concrete, realistic scenarios can help people better visualize the situation and make objective decisions about cybersecurity spending.
The European Community is among the governments that most strictly regulate data protection and cybersecurity enforcement in businesses. Regulations adopted in recent years tend to strengthen these requirements for players in strategic sectors and their suppliers (NIS 2 Directive), financial players (DORA Regulation), and companies that have adopted artificial intelligence (AI ACT).
Penalties for GDPR violations apply to all companies, regardless of size or sector.
Contrary to popular belief, the National Commission for Data Protection (CNPD) monitors SMEs as much as large companies, as evidenced by the list of decisions published on its website.
Remember that fines can range from 2% to 4% of the company’s global annual turnover, or from €10 million to €20 million, whichever is higher.
Here again, the calculation is simple : if the potential fine for non-compliance with regulations exceeds the cost of the proposed solutions, management will be more inclined to grant you the necessary budget.
Need advice on how to secure your business ?
Rather than an immediate investment, propose a gradual plan :
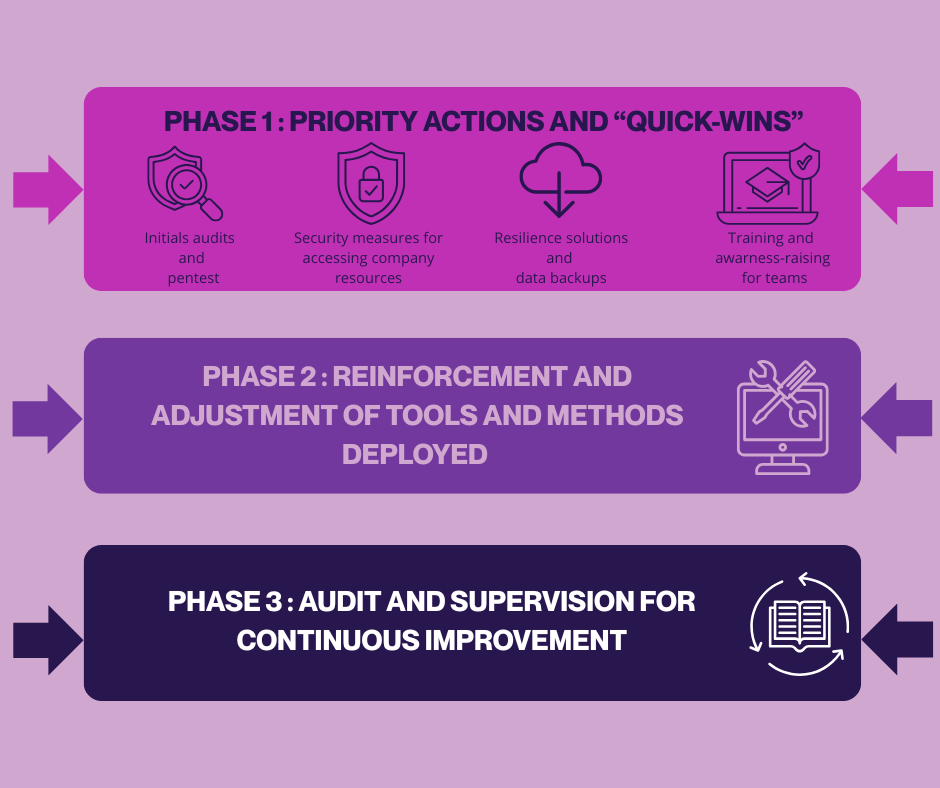
Your management will want to understand and be able to monitor the cybersecurity actions taken.
To do this, propose performance indicators and dashboards for managers and non-technical profiles: response time in the event of an incident, number of cyberattacks thwarted, improvement in employee scores during phishing campaigns, and reduction in the gaps between your practices and regulatory requirements.
If necessary, seek assistance from governance and audit experts. Rsecure’s shared-time CISOs are experts in regulatory frameworks (GDPR, NIS 2, DORA, FIDA) and recognized cybersecurity standards (ISO 27001, ISO 27005). We provide daily support for the deployment, management, and auditing of your governance and compliance projects.
Rsecure supports you in defining your needs, particularly in terms of cybersecurity investment.
Contact us today to discuss your requirements with our teams.